
A herniated disc is a common condition that can cause significant pain and discomfort. In an interview with Dr. Dmitri Souza from Western Reserve Hospital Center for Pain Medicine, we delve into the details of this condition, its causes, symptoms, risk factors, and available treatments.
What is a Herniated Disc?
To understand a herniated disc, it's essential first to know what spinal discs are. According to Dr. Souza, "Spinal discs are like small cushions between the vertebrae that make up the spine. They serve as shock absorbers for the spine, allowing it to bend, twist, and move comfortably." Each disc has two parts: the gel-like center called the nucleus and the tough exterior that encases the nucleus, called the annulus.
In the case of a herniated disc, "some of the nucleus pushes out through a tear in the annulus," Dr. Souza explains. This can irritate nearby nerves and result in symptoms such as pain, numbness, and weakness in the affected area.
Common Symptoms of a Herniated Disc
Identifying a herniated disc can be challenging, as symptoms vary depending on the location and severity of the herniation. Dr. Souza outlines several common signs and symptoms to watch for:
- Pain and numbness: Often localized to one side of the body.
- Pain that worsens with movements: Activities such as bending, lifting, or twisting can exacerbate the pain.
- Muscle weakness: Affected muscles may become weaker over time.
- Tingling and burning sensations: These can occur in the affected area.
- Radiating pain: Pain that extends to the arms or legs.
- Loss of bladder or bowel control: In severe cases, this can indicate a condition called cauda equina syndrome, which requires immediate medical attention.
"If you experience these symptoms, especially if they are severe, worsening, or persistent, it's important to consult with your physician," advises Dr. Souza.
Risk Factors and Causes
Understanding the underlying risk factors and causes of herniated discs can help in managing and preventing this condition. Dr. Souza identifies several key contributors:
- Age-related wear and tear: "Herniated discs are most common in people between the ages of 30 and 50," says Dr. Souza. As we age, spinal discs lose some of their water content, making them less flexible and more prone to tearing or rupturing. Degenerative disc disease, a gradual wear, is the most common cause of herniated discs.
- Injury or physical stress: "Heavy lifting or blunt trauma, like a fall or an accident, increases the risk of herniation," explains Dr. Souza.
- Repetitive motion: Jobs or activities involving repetitive motion, especially those involving lifting, pulling, bending, or twisting, can increase the risk of herniation.
- Chronic poor posture: This can put excessive stress on the spine and increase pressure on the discs.
- Lifestyle factors: Lack of exercise and a sedentary lifestyle can weaken the muscles supporting the spine. Obesity and smoking may also play a role.
- Genetics: There is some evidence that these problems can be inherited
"Addressing environmental factors like ergonomic practices and maintaining a healthy weight can help manage and potentially reduce the risk of herniation, especially in those who are genetically predisposed," advises Dr. Souza.
Preventing Herniated Discs
While not all cases of herniated discs can be prevented, certain lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk. Dr. Souza recommends the following preventative measures:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Reducing excess body weight can alleviate pressure on the spine.
- Exercise regularly: Strengthening the muscles that support the spine can prevent disc herniation.
- Practice good posture: Proper posture can minimize stress on the spine.
- Lift properly: Use proper techniques when lifting heavy objects to avoid straining the spine.
- Quit smoking: Smoking cessation can help improve overall disc health.
- Avoid repetitive stress: Minimize activities that put repetitive strain on the spine.
- Stay hydrated: Adequate hydration helps maintain disc flexibility.
"By incorporating these practices into daily life, one can help keep the spine healthy and potentially reduce the risk of developing a herniated disc," says Dr. Souza.
Treatments for Herniated Discs
For those experiencing mild symptoms of a herniated disc, there are several home treatments that can provide relief. At home treatments include staying active as extended inactivity can worsen the condition. Heat or ice as well as over the counter pain medications can help manage pain and inflammation as well. It is also important to avoid activities that worsen the pain. "If symptoms persist or worsen, or if someone experiences severe symptoms such as numbness, weakness, or loss of bladder or bowel control, it is important to seek immediate medical guidance," emphasizes Dr. Souza.
For more severe cases, medical intervention may be necessary. Dr. Souza outlines the two primary types of treatment: conservative and surgical.
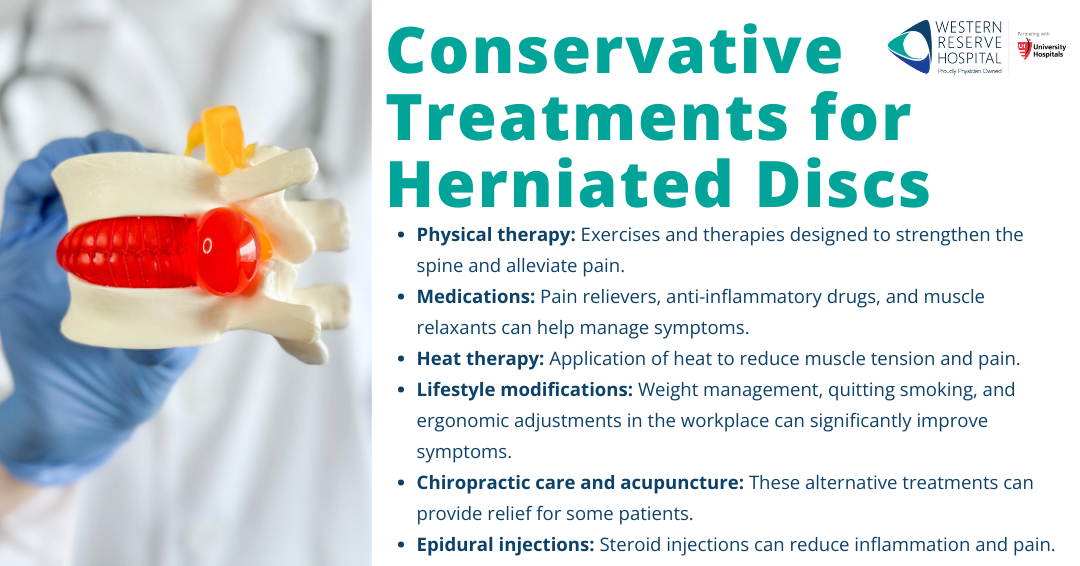
Conservative Treatments
- Physical therapy: Exercises and therapies designed to strengthen the spine and alleviate pain.
- Medications: Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and muscle relaxants can help manage symptoms.
- Heat therapy: Application of heat to reduce muscle tension and pain.
- Lifestyle modifications: Weight management, quitting smoking, and ergonomic adjustments in the workplace can significantly improve symptoms.
- Chiropractic care and acupuncture: These alternative treatments can provide relief for some patients.
- Epidural injections: Steroid injections can reduce inflammation and pain.
Surgical Treatments
Surgery is considered if conservative treatments fail to relieve symptoms or if the patient experiences worsening neurological symptoms. Dr. Souza explains that common surgical options include:
- Discectomy or microdiscectomy: Removal of the herniated portion of the disc to relieve nerve pressure.
- Laminectomy: Removal of part of the bone covering the spinal canal to create more space for the nerves.
- Artificial disc replacement: Replacement of the damaged disc with an artificial one.
- Spinal fusion: Joining two or more vertebrae together to stabilize the spine.
"Surgery is an important treatment tool, especially when conservative treatments are ineffective," says Dr. Souza. "It's essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan based on individual needs and circumstances."
Can Herniated Discs Be Healed?
The body's response to a herniated disc includes a natural process where the protruded part of the disc may shrink over time. "While the rupture in the disc may not completely heal back to its original condition, many people can return to a normal level of functioning without persistent pain," explains Dr. Souza. It is essential for anyone with persistent symptoms due to a herniated disc to consult with their physician to get a personalized treatment plan.
When to See a Doctor
Certain symptoms may indicate a serious condition that requires medical attention. Dr. Souza advises seeing a doctor if you experience:
- Persistent pain: Pain that does not improve with home treatment.
- Pain radiating to arms or legs: This could indicate nerve involvement.
- Loss of function: Limping or other gait instabilities.
- Loss of sensation: Changes in reflexes or sensation in the limbs.
- Problems with bladder or bowel control: This could indicate a serious condition requiring immediate attention.
- Night pain: Pain that worsens at night may indicate a progressive condition.
"It is advisable to see a physician for a comprehensive evaluation and timely management to prevent further complications and preserve quality of life," concludes Dr. Souza.
A herniated disc can be a painful and debilitating condition, but with proper understanding and management, most people can find relief and return to normal activities. At Western Reserve Hospital’s Center for Pain Medicine, doctors utilize comprehensive treatment plans for patients experiencing pain related to a herniated disc. Dr. Souza is a board-certified physician who specializes in pain medicine, anesthesiology, internal medicine, and headache medicine.
Looking for treatment for pain that could be related to a herniated disc? Reach out to Dr. Souza to set up a consultation to explore treatment options.
